ASTM F1941 Specification
- Scope
- Terminology
- Classification
- Ordering Information for Electroplating
- Dimensional Requirements
- Sampling
- Test Methods
- Electroplating Processes
- Other Information
- Referenced Documents
- Designation of Common Coating Materials
- Designation of Coating Thickness
- Designation of Chromate Finish
- Coating Requirements The electrodeposited coating as ordered shall cover all surfaces and shall meet the following requirements:
- Corrosion Resistance Coated fasteners, when tested by continuous exposure to neutral salt spray in accordance with 9.3, shall show neither corrosion products of coatings (white corrosion) nor basis metal corrosion products (red rust) at the end of the test period. The appearance of corrosion products visible to the unaided eye at normal reading distance shall be cause for rejection, except when present at the edges of the tested fasteners. Refer to Annex A1 for neutral salt spray performance requirements for zinc, zinc alloy and cadmium coatings.
- Thickness The coating thickness shall comply with requirements of Table 2 when measured in accordance with 9.1.
- Hydrogen Embrittlement Relief:
- Non-Hexavalent Passivate Finishes The use of hexavalent chromium is prohibited when processing coated fasteners to the requirement of 4.3.1.1. Coated fasteners shall be free of hexavalent chromium when tested in accordance with the test method defined in 9.4.
- Coating Thickness — Unless otherwise specified, the requirement to measure coating thickness is applicable to significant surfaces only. The test methods for determining the coating thickness are defined in Test Methods B487, B499, B504, B567, B568, Guide B659, or Practice E376 as applicable.
- Embrittlement Test Method — The embrittlement test method shall conform to those specified in Test Methods F1940 for process verification, or F606, F1624, or NASM-1312-5 for product testing.
- Corrosion Resistance — The requirement to determine corrosion resistance is applicable to significant surfaces only. When specified in the contract or purchase order, a salt spray test shall be conducted in accordance with Practice B117. To secure uniformity of results, samples shall be aged at room temperature for 24 h before being subjected to the salt spray test.
- Non-Hexavalent Passivate Finish — The presence of hexavalent chromium shall be determined in accordance with Practice D6492.
- NEUTRAL SALT SPRAY PERFORMANCE:
- Classification Code and Neutral Salt Spray Corrosion Protection Performance of Zinc and Cadmium Coatings
- Classification Code and Neutral Salt Spray Protection of Zinc Coatings with Non-Hexavalent Supplemental Passivate Finish
- Classification Code and Neutral Salt Spray Corrosion Protection Performance of Zinc-Cobalt Coatings
- Classification Code and Neutral Salt Spray Corrosion Protection Performance of Zinc-Nickel Coatings
- Classification Code and Neutral Salt Spray Corrosion Protection Performance of Zinc-Iron Coatings
- Standard electrodeposition process
- Guidelines for choosing between barrel-plating and rack-plating
- Coating accommodation tolerances for externally and internally threaded fasteners
- Application requirements
- Use of trivalent chromium (Cr+3) on coated fasteners
This specification covers application, performance and
dimensional requirements for electrodeposited coatings on
threaded fasteners with unified inch screw threads. It specifies
coating thickness, supplementary hexavalent chromate or non-hexavalent passivate finishes, corrosion
resistance, precautions
for managing the risk of hydrogen embrittlement and hydrogen
embrittlement relief for high-strength and surface-hardened
fasteners. It also highlights the differences between barrel and
rack plating and makes recommendations as to the applicability
of each process.
The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
The following precautionary statement pertains to the
test method portion only, Section 9, of this specification: This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Terminology
Definitions:
Local thickness—the mean of the thickness measurements, of which a specified number is made within
a reference
area.
Minimum local thickness—the lowest local thickness
value on the significant surface of a single article.
Reference area—the area within which a specified
number of single measurements are required to be made.
Significant surface—significant surfaces are areas
where the minimum thickness to be met shall be designated on
the applicable drawing or by the provision of a suitably marked
sample. However, if not designated, significant surfaces shall
be defined as those normally visible, directly or by reflection,
which are essential to the appearance or serviceability of the
fastener when assembled in normal position, or which can be
the source of corrosion products that deface visible surfaces on
the assembled fastener. Figs. 1 and 2 illustrate significant
surfaces on standard externally threaded and internally
threaded fasteners.
Classification
Coating Material— The coating material shall be selected and designated in accordance with Table.
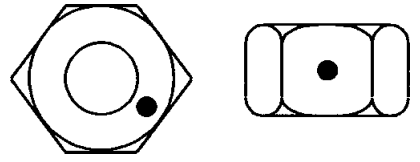
Note 1- Black dot (.) indicates test surface.
Figure 1 — Significant
Surfaces on Internally Threaded Fasteners
| Coating Designation | Coating Type |
|---|---|
| Fe/Zn | Zinc |
| Fe/Cd | Cadmium |
| Fe/Zn-Co | Zinc Cobalt Alloy |
| Fe/Zn-Ni | Zinc Nickel Alloy |
| Fe/Zn-Fe | Zinc Iron Alloy |
Coating Thickness—The coating thickness shall be
selected and designated in accordance with Table:
Chromate Finish—When not specified, the hexavalent,
trivalent or other chromiate finish shall be used at the option of
the manufacturer and its appearance shall be selected in
accordance with the designation selected in Table.
Passivate—for the purpose of this specification, a
conversion coating shall not contain hexavalent chromium.
Trivalent Chromite Passivate Finish—Unless otherwise specified, the typical appearance of the
trivalent chromite
finish shall be transparent, colorless and shall not be subjected
to the requirements of typical appearance as determined in
Table. In addition, the classification code to be used
shall be
appended with the letter 9T9 (for example, Fe/Zn 5CT, as
defined in Table A1.1 ).
Supplemental Passivate Finish —Unless otherwise
specified, the typical appearance of the supplemental passivate
finish shall be transparent, colorless and shall not be subjected
to the requirements of typical appearances as determined in
Table. In addition, the classification code to be used
shall be
appended with the letter “S” (for example Fe/Zn 5AS). Other
colored finishes may be specified at time of purchase. Requirements of the other colored finishes to
be agreed upon at time of
purchase.
Note 1 — The conversion factor from inch to microns is 2.54 3 104 (for example, 0.0001 in. = 2.54 µm).
| Thickness Designation | Minimum Thickness in. |
|---|---|
| 3 | 0.0001 |
| 5 | 0.0002 |
| 8 | 0.0003 |
| 12 | 0.0005 |
Note 1 — Coated fasteners with trivalent chromite (Cr+3) are not
subjected to the required yellow, opaque, and black color. See Appendix
X5.
Note 2 — When fasteners are coated with trivalent chromite (Cr+3) the
classification code to be used shall be appended with the letter 9T9 .
| Designation | Type | Typical Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| A | Clear | Transparent colorless with slight iridescence |
| B | Blue-bright | Transparent with a bluish tinge and slight iridescence |
| C | Yellow | Yellow iridescent |
| D | Opaque | Olive green, shading to brown or bronze |
| E | Black | Black with slight iridescence |
| F | Organic | Any of the above plus organic topcoat |
Note 1 — The use of supplemental passivated finishes are technically not “chromate” films and they do not contain hexavalent chromium ions, they are supplemental coatings that render the active zinc surface passive and provide protection to the steel fastener.
Ordering Information for Electroplating
When ordering threaded fasteners to be coated by
electrodeposition in accordance with this specification, the
following information shall be supplied to the electroplater:
The desired coating, coating thickness, the chromate
or passivate finish, the color and appearance (if applicable), or
the classification codes as specified in Tables 1-3. (for example,
Fe/Zn 5C denotes yellow zinc plated with a minimum thickness of 0.0002 in. on significant surfaces.)
The identification of significant surfaces (optional).
The requirement, if any, for stress relief before electroplating, in which case the stress-relief
conditions must be
specified.
The requirements, if any, for hydrogen embrittlement
relief by heat treatment (baking) stating the tensile strength or
surface hardness of the fasteners and/or baking time and
temperature.
Note 2 — Fasteners with a specified maximum hardness of 34 HRC and
below have a very low susceptibility to hydrogen embrittlement and do
not require baking.
The requirements, if any, for the type of electroplating
process (barrel-plating or rack-plating). See Section 10 and
Appendix X1.
The designation of coated thread class shall comply
with ASME B1.1.
Requirements
The coating metal deposit shall be bright or semi-bright unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, smooth, fine grained, adherent and uniform in appearance.
The coating shall be free of blisters, pits, nodules, roughness, cracks, unplated areas, and other defects that will affect the function of the coating.
The coating shall not be stained, discolored or exhibit any evidence of white or red corrosion products.
6.1.3.1 Slight discoloration that results from baking, drying, or electrode contact during rack-plating, or all of these, as well as slight staining that results from rinsing shall not be cause for rejection.
Restrictions on Coating Thickness—This specification imposes minimum local thickness requirements at significant surfaces in accordance with Table 2. Thick or thin local thickness in a location other than a significant surface shall not be a cause for rejection. However the following restrictions apply:
Minimum coating thickness at low current density areas, such as the center of a bolt or recesses, must be sufficient to provide for adequate chromate adhesion.
External Threads — Maximum coating thickness at high current density threaded tips must provide for class 3A GO thread gauge acceptance.
Internal Threads — Maximum coating thickness of internal threads must provide for class 1B, 2B, or 3B Go thread gage acceptance.
Surfaces such as threads, holes, deep recesses, bases of angles, and similar areas on which the specified thickness of deposit cannot readily be controlled, are exempted from minimum thickness requirements unless they are specially designated as not being exempted. When such areas are subject to minimum thickness requirements, the purchaser and the manufacturer shall recognize the necessity for either thicker deposits on other areas or special racking.
Applicability to Unified Inch Screw Threads:
The applicability of the required coating to unified inch screw threads is limited by the basic deviation of the threads, and hence limited by the pitch diameter, allowance and tolerance positions. Refer to Appendix X3 as a guideline for the tolerances of the various thread sizes and classes and the coating thickness they will accommodate.
Because of the inherent variability in coating thickness by the barrel-plating process, the application of a minimum coating thickness of 0.0005 in. is not recommended for a standard screw thread by this method due to the fact that dimensional allowance of most threaded fasteners normally does not permit it. If the size of the fastener is large enough to economically use the rack-plating process, then the latter shall be used to obtain this thickness requirement. If heavier coatings are required allowance for the deposit buildup must be made during the manufacture of fasteners.
Applicability to Wood Screws and Thread Forming Screws—Any classification code in Table 2 may be applied to screws that cut or form their own threads.
For Supplemental Passivate Finishes, the minimum recommended zinc thickness is 5µm.
Requirement for Baking—Coated fasteners made from steel heat treated to a specified hardness of 40 HRC or above, case-hardened steel fasteners, and fasteners with captive washers made from hardened steel shall be baked to minimize the risk of hydrogen embrittlement. Unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, baking is not mandatory for fasteners with specified maximum hardness below 40 HRC.
NOTE 3 — With proper care many steel fasteners can be plated without baking by correlating process conditions to the susceptibility of the fastener material to hydrogen embrittlement, and by applying adequate process control procedures, such as those outlined in Appendix X4.2. Test Method F1940 is a recognized verification method for process control to minimize the risk of hydrogen embrittlement. Upon agreement between the supplier and the purchaser, this test method can be used as a basis for determining if baking should be mandated in a controlled process environment.
Baking Conditions — At the time of publication of this specification it was not considered possible to give an exact baking duration. Eight hours is considered a typical example of baking duration. However, upon agreement between the purchaser and the manufacturer, baking times between 2 and 24 h at temperatures of 350 to 450°F are suitable depending on the type and size of the fastener, geometry, mechanical properties, cleaning process and cathodic efficiency of the electroplating process used. The baking conditions shall be selected based on the results of recognized embrittlement test procedures such as Test Methods F606, F1624, F1940, or NASM–1312–5.
Bake time and temperatures may require lowering to minimize the risk of solid or liquid metal embrittlement resulting from alloy compositions such as those containing lead or from the lower melting point of cadmium (610°F) in comparison to zinc (786°F).
Fasteners must be baked within 4 h, preferably 1 h after electroplating. Baking to relieve hydrogen embrittlement must be performed prior to the application of the chromate finish because temperatures above 150°F damage the chromate film thereby negating its performance.
Hydrogen Embrittlement Testing—Hydrogen embrittlement testing is mandatory for fasteners with a specified hardness of 40 HRC or above unless the electroplating process has been qualified in accordance with Test Method F1940 (that is, the process has been shown not to cause embrittlement for a given product or class of product). This specification does not require mandatory testing of fasteners having a specified hardness below 40 HRC, unless otherwise specified by the purchaser.
Dimensional Requirements
Threaded components, except those with spaced and forming threads, supplied for electrodeposited coating shall comply with ASME B1.1. Screw threads that are specifically manufactured to allow the application of 0.0005 in. or greater coating thickness by the barrel-plating process, must adhere to a special allowance specified by the manufacturer or in ASME B1.1. The other dimensional characteristics shall be as specified in the applicable standard or drawing. It should be noted that modifications to the threads of a fastener could affect its properties or performance, or both. Refer to Appendix X3 for further information on effects of coating on pitch diameter, allowances and tolerances for external and internal threads.
Sampling
Sampling for coating thickness, salt spray and embrittlement testing shall be conducted based on lot size in accordance with Guide F1470.
Test Methods
Electroplating Processes
Two electroplating processes are most commonly used to apply a metallic coating by electrodeposition on threaded fasteners: barrel-plating and rack-plating. When thread fit or thread integrity, or both, is a concern for externally threaded fasteners, rack-plating is preferable to barrel-plating. Refer to Appendix X1.
See Table A1.1, Table A1.2, Table A1.3, Table A1.4, and Table A1.5.
NOTE — When fasteners are coated with trivalent chromite (Cr+3), the classification code to be used shall be appended with the letter "T".
| Classification Code | Minimum Coating Thickness, in. |
Chromate Finish Designation | First Appearance of White Corrosion Product, (hour) |
First Appearance of Red Rust Cadmium, (hour) |
First Appearance of Red Rust Zinc, (hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 3A | 0.0001A | A | 3 | 24 | 12 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 3B | --- | B | 6 | 24 | 12 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 3C | --- | C | 24 | 36 | 24 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 3D | --- | D | 24 | 36 | 24 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 5A | 0.0002 | A | 6 | 48 | 24 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 5B | --- | B | 12 | 72 | 36 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 5C | --- | C | 48 | 120 | 72 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 5D | --- | D | 72 | 168 | 96 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 5E | --- | E | 12 | 72 | |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 8A | 0.0003 | A | 6 | 48 | 24 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 8B | --- | B | 12 | 72 | 36 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 8C | --- | C | 48 | 120 | 72 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 8D | --- | D | 72 | 168 | 96 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 8E | --- | E | 12 | 72 | |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 12A | 0.0005 | A | 6 | 144 | 72 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 12B | --- | B | 24 | 192 | 96 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 12C | --- | C | 72 | 240 | 144 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 12D | --- | D | 96 | 264 | 168 |
| Fe/Zn or Fe/Cd 12Bk | --- | E | 24 | 192 | 96 |
| A Low coating thickness impairs chromate adhesion and performance. | |||||
NOTE — When fasteners are coated with supplemental non-hexavalent passivate finish, the classification code to be used shall be appended with the letter “S”.
| Classification Code | Minimum Coating Thickness, in. |
Chromate Finish Designation |
First Appearance of Zinc Alloy Corrosion Product (hour) |
First Appearance of Red Rust (hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/Zn 5AS | 0.0002 | A | 96 | 120 |
| Fe/Zn 8AS | 0.0003 | --- | --- | --- |
| Fe/Zn 12AS | 0.0005 | --- | --- | --- |
| Classification Code | Minimum Coating Thickness, in. |
Chromate Finish Designation |
First Appearance of Zinc Alloy Corrosion Product (hour) |
First Appearance of Red Rust (hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/Zn-Co 5C | 0.0002 | C | 96 | 240 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 5D | --- | D | 96 | 240 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 5E | --- | E | 100 | 240 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 5F | --- | F | 196 | 340 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 8C | 0.0003 | C | 96 | 240 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 8D | --- | D | 96 | 240 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 8E | --- | E | 100 | 240 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 8F | --- | F | 200 | 340 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 12B | 0.0005 | B | 12 | 240 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 12C | --- | C | 96 | 400 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 12D | --- | D | 96 | 400 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 12E | --- | E | 100 | 400 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 12F | --- | F | 196 | 500 |
| Classification Code | Minimum Coating Thickness, in. |
Chromate Finish Designation |
First Appearance of Zinc Alloy Corrosion Product (hour) |
First Appearance of Red Rust (hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/Zn-Ni 5B | 0.0002 | B | 20 | 150 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 5C | --- | C | 120 | 500 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 5D | --- | D | 180 | 750 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 5E | --- | E | 100 | 500 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 5B/F | --- | B/F | 150 | 300 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 5C/F | --- | C/F | 240 | 620 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 5D/F | --- | D/F | 300 | 1000 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 5E/F | --- | E/F | 220 | 620 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 8B | 0.0003 | B | 20 | 240 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 8C | --- | C | 120 | 720 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 8D | --- | D | 180 | 960 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 8E | --- | E | 100 | 720 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 8B/F | --- | B/F | 150 | 400 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 8C/F | --- | C/F | 240 | 840 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 8D/F | --- | D/F | 300 | 1200 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 8E/F | --- | E/F | 220 | 840 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 12B | 0.0005 | B | 20 | 500 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 12C | --- | C | 120 | 960 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 12D | --- | D | 180 | 1000 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 12E | --- | E | 100 | 960 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 12B/F | --- | B/F | 150 | 620 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 12C/F | --- | C/F | 240 | 1080 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 12D/F | --- | D/F | 300 | 1500 |
| Fe/Zn-Ni 12E/F | --- | E/F | 220 | 1080 |
| Classification Code | Minimum Coating Thickness, in. |
Chromate Finish Designation |
First Appearance of Zinc Alloy Corrosion Product (hour) |
First Appearance of Red Rust (hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/Zn-Co 5E | 0.0002 | E | 144 | 312 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 8E | 0.0003 | E | 144 | 312 |
| Fe/Zn-Co 12E | 0.0005 | E | 144 | 480 |
Other Information
Referenced Documents
Referenced Documents
ASTM Standards:
B117 Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus
B487 Test Method for Measurement of Metal and Oxide
Coating Thickness by Microscopical Examination of Cross
Section
B499 Test Method for Measurement of Coating Thicknesses by
the Magnetic
Method: Nonmagnetic
Coatings on
Magnetic Basis Metals
B504 Test Method for Measurement of Thickness of Metallic
Coatings by the
Coulometric Method
B567 Test Method for Measurement of Coating Thickness
by the Beta Backscatter Method
B568 Test Method for Measurement of Coating Thickness
by X-Ray Spectrometry
B659 Guide for Measuring Thickness of Metallic and
Inorganic Coatings
D6492 Practice for Detection of Hexavalent Chromium On
Zinc and Zinc/Aluminum Alloy Coated Steel
E376 Practice for Measuring Coating Thickness by
Magnetic-Field or Eddy-Current (Electromagnetic) Examination Methods
F606 Test Methods for Determining the Mechanical
Properties of Externally
and Internally Threaded
Fasteners,
Washers, Direct Tension Indicators, and Rivets
F1470 Practice for Fastener Sampling for Specified
Mechanical Properties
and Performance Inspection
F1624 Test Method for Measurement of Hydrogen
Embrittlement Threshold in
Steel by the Incremental
Step
Loading Technique
F1940 Test Method for Process Control Verification to
Prevent Hydrogen Embrittlement in Plated or Coated
Fasteners
ASME Standard:
B1.1 Unified Inch Screw Threads (UN and UNR Thread
Form)
National Aerospace Standard (AIA):4
NASM-1312-5 Fast Test Method - Method 5: Stress Durability
IFI Standard:
IFI-142 Hydrogen Embrittlement Risk Management