ISO 10684 Specification
- Scope
- Materials
- Hot dip galvanizing procedures and precautions
- Requirements on thread tolerances and additional marking
- Fundamental deviations and upper limits of coating thicknesses for assemblies with nuts tapped oversize
- Fundamental deviations and upper limits of coating thicknesses for assemblies with bolts and screws with undersized threads
- Mechanical properties of nuts tapped oversize and undersize threaded bolts, screws and studs
- Coating requirements
- Lubrication
- Ordering requirements
- Other Informations
- Terminology
- Normative Reference
ISO 10684 International Standard specifies material, process, dimensional and some performance
requirements for hot dip spun galvanized coatings applied to coarse threaded steel fasteners from M8 up
to and including M64 and for property classes up to and including 10.9 for bolts, screws and studs and
12 for nuts. It is not recommended to hot dip galvanize threaded fasteners in diameters smaller than M8
and/or with pitches below 1.25 mm.
NOTE Attention is drawn to the fact that the proof loads and stresses under proof load of oversize
tapped nuts with threads M8 and M10 and the ultimate tensile loads and proof loads of undersize threaded
bolts and screws with threads M8 and M10 are reduced as compared to the values specified in ISO 898-2
and ISO 898-1 respectively and are
specified in Annex A.
It primarily concerns the spun hot dip galvanizing of threaded steel fasteners, but it may also be
applied to other threaded steel parts.
The specifications given in this International Standard may also be applied to non-threaded steel parts
such as washers.
Materials
Raw material of parts- Chemical composition
- Surface condition
Materials as included in ISO 898-1 and ISO 898-2 are suitable for hot dip galvanizing except if the total content of phosphorus and silicon is between 0.03 % and 0.13 %, in which case high temperature galvanizing (530°C to 560°C) is recommended.
The surface of the fastener, before immersion in the molten zinc, shall be clean and free from all contaminants that would adversely effect the galvanizing.
- Chemical composition
The zinc used for this process shall be in accordance with ISO 1461.
Hot dip galvanizing procedures and precautions
- Stress relief
- Cleaning and pickling
- Baking
- Fluxing
- Hot dip galvanizing
- Spinning and quenching
- Special requirements for nuts
- Post-treatment
Fasteners subjected to severe work hardening may require stress relief before acid cleaning and hot dip galvanizing.
Parts shall be cleaned. During the cleaning process, hydrogen could be absorbed into the steel. The hydrogen may not effuse completely in the galvanizing bath and consequently, may lead to brittle failure. Unless otherwise agreed, parts heat treated or work hardened to a hardness of ≥ 320 HV shall be cleaned using an inhibited acid, alkaline or mechanical process. Immersion time in the inhibited acid depends on the as-received surface condition and should be of minimum duration.
NOTE- An inhibited acid is an acid to which a suitable inhibitor has been added to reduce corrosive attack on the steel and absorption of hydrogen.
If baking is carried out, it shall be carried out prior to surface activation.
Parts shall be surface activated, and dried if necessary
Normal temperature galvanizing is carried out at a bath temperature of 455°C to 480 °C. High
temperature galvanizing is used to produce a smoother and thinner coating and is carried out at a bath
temperature of 530°C to 560 °C. The finish obtained using the high temperature process is dull. In
order
to avoid microcracks, bolts, screws and studs of property class 10.9 in sizes M27 and above, shall not
be high temperature galvanized.
Galvanizing shall not be carried out at bath temperatures between 480°C and 530 °C.
Parts shall be spun immediately following removal from the galvanizing bath and quenched in water or air cooled depending on size consideration.
Nut threads and other internal threads shall be tapped after hot dip galvanizing. Retapping shall not be permitted.
Most galvanized parts do not require any post treatment. When required by the purchaser, treatments such as chromating or phosphating may be applied to reduce the possibility of wet storage staining (white corrosion) or to assist subsequent painting.
Requirements on thread tolerances and additional marking
- General
- General
- Nuts tapped oversize to tolerance class 6AZ or 6AX after coating.
- Bolts and screws with threads undersized to tolerance class 6az before coating.
- Appearance of zinc coating
- Considerations for hot dip galvanized washers
- Zinc coating thickness
- Adhesion of zinc coating
- Special requirements for bolts, screws and nuts with thread sizes M8 and M10
- Limits of sizes for hot dip galvanized internal and external screw thread M8
- Calculation of minimum ultimate tensile loads and proof loads for bolts and screws M8 and M10 with threads undersized to tolerance class 6az
- Surface areas of bolts, screws and nuts
- Adherence of hot-dip galvanized coating
- Strength of hot dip galvanized bolt or screw and nut assemblies
- batch
- production lot
- batch average thickness
- baking
- stress relief
- hot dip galvanizing of fasteners
- NOTE:-
This process involves the removal of excess zinc by spinning the parts in a centrifuge or by an equivalent method.
Dimensional limits for ISO metric screw threads M10 to M64 before and after coating are specified in ISO 965-1 to ISO 965-5. All other dimensions and tolerances of fasteners apply before hot dip galvanizing. Dimensional limits for internal and external screw threads M8 with thread tolerances 6AX and 6AZ for internal threads and 6az for external threads are specified in Annex B.
NOTE- It is not possible to check the thread tolerance of a hot dip galvanized part by stripping the coating and gauging the thread thereafter, since some steel is dissolved from the part during the galvanizing process.Requirements and precautions in assembling hot dip galvanized threaded fasteners
This clause applies only to parts with thread tolerances in accordance with
ISO 965-1 to
ISO 965-5 and with marking according to the marking
requirements for fasteners as given in
ISO 898-1 and
ISO 898-2.
The marking specified in 2 points and 3 points
shall be carried out in addition to the marking according to
ISO 898-1 and
ISO 898-2.
The application of zinc coating by the hot dip process results in the deposition of a heavy coating
thickness of zinc (always in excess of 40 iJm). Hence, it is necessary to manufacture screw threads
to special limits in order to accommodate such heavy coatings.
There are two different methods provided for, which give the necessary fundamental deviations
(clearances) for the zinc layer applied to fasteners by hot dip galvanizing.
The first method (see 2 points) consists of using nuts tapped oversize to
tolerance class 6AZ or 6AX
after coating, to mate with bolts or screws manufactured with screw threads to tolerance position g
or h before coating.
The second method (see 3 points) consists of using bolts or screws
manufactured with threads undersized
to tolerance class 6az before coating, to mate with nuts tapped to tolerance position H or G after
coating.
Nuts tapped oversize (marked with Z or X) shall never be mated with bolts or screws with
undersized threads (marked with U), because such combinations create a high probability of thread
stripping.
Assembling hot dip galvanized nuts tapped to tolerance position H or G after coating with hot dip
galvanized bolts or screws manufactured with threads to tolerance position 9 or h before coating
results in thread interference.
Oversize tapping of nuts and internal threads to tolerance class 6AZ or 6AX in accordance with
ISO 965-5 is required after hot dip galvanizing when the
mating bolts or screws or external threads are manufactured to tolerance position g or h in
accordance with ISO 965-1 to
ISO 965-3 before hot dip galvanizing.
Nuts tapped oversize shall be marked with the letter Z immediately after the property class mark in
case of tolerance class 6AZ or with the letter X in case of tolerance class 6AX. See example in
below Figure.
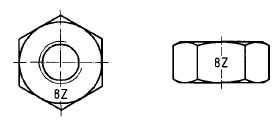
Example of marking of hot dip galvanized nuts tapped oversize to tolerance position 6AZ after coating
In order to reduce the risk of interference on assembly of threads with hot dip galvanized coatings, the coating thickness on the mating bolts or screws or external threads advisably should not exceed one quarter of the minimum clearance of the thread combination. These values are given in below Table for information.
Fundamental deviations and upper limits of coating thicknesses for assemblies with nuts tapped oversize
| Pitch | Nominal thread diameter | Fundamental deviation | Minimum clearance and maximum coating thickness for thread
combinations (for information) |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal thread | External thread | AZ/h | AZ/g | AX/h | AX/g | ||||||||
| p | d | AZ | AX | h | g | Minimum clearance | Maximum coating thickness | Minimum clearance | maximum coating thickness | Minimum clearance | maximum coating thickness | Minimum clearance | maximum coating thickness |
| mm | mm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm |
| 1.25 | 8 | +325a | +255a | 0 | -28 | 325 | 81 | 353 | 88 | 255 | 64 | 283 | 71 |
| 1.5 | 10 | +330 | +310 | 0 | -32 | 330 | 83 | 362 | 91 | 310 | 78 | 342 | 86 |
| 1.75 | 12 | +335 | +368 | 0 | -34 | 335 | 84 | 369 | 92 | 365 | 91 | 399 | 100 |
| 2 | 16 (14) | +340 | +420 | 0 | -38 | 340 | 85 | 378 | 95 | 420 | 105 | 458 | 115 |
| 2.5 | 20 (18.22) | +350 | +530 | 0 | -42 | 350 | 88 | 392 | 98 | 530 | 133 | 572 | 143 |
| 3 | 24 (27) | +360 | +640 | 0 | -48 | 360 | 90 | 408 | 102 | 640 | 160 | 688 | 172 |
| 3.5 | 30 (33) | +370 | +750 | 0 | -53 | 370 | 93 | 423 | 106 | 750 | 188 | 803 | 201 |
| 4 | 36 (39) | +380 | +860 | 0 | -60 | 380 | 95 | 440 | 110 | 860 | 215 | 920 | 230 |
| 4.5 | 42 (45) | +390 | +970 | 0 | -63 | 390 | 98 | 453 | 113 | 970 | 243 | 1033 | 258 |
| 5 | 48 (52) | +400 | +1080 | 0 | -71 | 400 | 100 | 471 | 118 | 1080 | 270 | 1151 | 288 |
| 5.5 | 56 (60) | +410 | +1190 | 0 | -75 | 410 | 103 | 485 | 121 | 1190 | 398 | 1265 | 316 |
| 6 | 64 | +420 | +1300 | 0 | -80 | 420 | 105 | 500 | 125 | 1300 | 325 | 1380 | 345 |
|
A The fundamental deviations for AZ and AX are calculated according to the formulae given in ISO 965-5 on the basis of the thread dimensions specified in Annex B. |
|||||||||||||
Undersize threading of bolts, screws and external threads to tolerance class 6az in accordance with
ISO 965-4 is required before hot dip galvanizing, when
the mating nuts or internal threads have tolerance position G or H in accordance with
ISO 965-1 to
ISO 965-3 after hot dip galvanizing.
Bolts and screws with undersized threads shall be marked with the letter U immediately after the
property class mark. See example in below Figure.
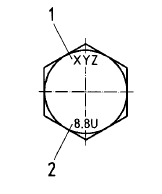
Key:
1. manufacture's identification mark
2. property class and additional marking
Example of marking of hot dip galvanized bolts and screws with threads undersized to tolerance class 6az before coating
In order to reduce the risk of interference on assembly of threads with hot dip galvanized coatings, the coating thickness advisably should not exceed one quarter of the minimum clearance of the thread combination. These values are given in below Table for information.
Fundamental deviations and upper limits of coating thicknesses for assemblies with bolts and screws with undersized threads
| Pitch | Nominal thread diameter | Fundamental deviation | Minimum clearance and maximum coating thickness for thread
combinations (for information) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| External thread | Internal thread | az/H | az/G | |||||||
| p | d | az | H | G | Minimum clearance | Maximum coating thickness | Minimum clearance | maximum coating thickness | ||
| mm | mm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | μm | ||
| 1.25 | 8 | + 325a | 0 | -28 | 325 | 81 | 353 | 88 | ||
| 1.5 | 10 | +330 | 0 | -32 | 330 | 83 | 362 | 91 | ||
| 1.75 | 12 | +335 | 0 | -34 | 335 | 84 | 369 | 92 | ||
| 2 | 16 (14) | +340 | 0 | -38 | 340 | 85 | 378 | 95 | ||
| 2.5 | 20 (18.22) | +350 | 0 | -42 | 350 | 88 | 392 | 98 | ||
| 3 | 24 (27) | +360 | 0 | -48 | 360 | 90 | 408 | 102 | ||
| 3.5 | 30 (33) | +370 | 0 | -53 | 370 | 93 | 423 | 106 | ||
| 4 | 36 (39) | +380 | 0 | -60 | 380 | 95 | 440 | 110 | ||
| 4.5 | 42 (45) | +390 | 0 | -63 | 390 | 98 | 453 | 113 | ||
| 5 | 48 (52) | +400 | 0 | -71 | 400 | 100 | 471 | 118 | ||
| 5.5 | 56 (60) | +410 | 0 | -75 | 410 | 103 | 485 | 121 | ||
| 6 | 64 | +420 | 0 | -80 | 420 | 105 | 500 | 125 | ||
|
AThe fundamental deviation for az is calculated according to the formula given in ISO 965-4 on the basis of the thread dimensions specified in Annex B. |
||||||||||
If hot dip galvanized bolts or screws and mating nuts are packed together and supplied in the
manufacturer's sealed container, the additional marking of the bolts, screws or nuts as described in
2 points and 3 points is not mandatory. The label on
each sealed container shall indicate the additional marking as required in
2 points and 3 points.
Additional marking of products or labelling of containers as described in
2 points and 3 points is not mandatory for fasteners
with a special marking related to a product standard which specifies the thread tolerance for hot dip
galvanized bolts, screws, studs or nuts and, therefore, does not allow the manufacturer to choose the
thread tolerance.
Mechanical properties of nuts tapped oversize and undersize threaded bolts, screws and studs
For bolts, screws, studs and nuts ~ M12, the requirements of ISO 898-1 and ISO 898-2 shall be met after hot dip galvanizing. For the sizes M8 and M10, proof loads and stresses under proof loads for nuts and ultimate tensile loads and proof loads for bolts, screws and studs are specified in Annex A.
Coating requirements
The hot dip galvanized parts shall be free from uncoated areas, blisters, flux deposits, black spots, dross inclusions and other defects that would impair the intended use of the parts. Dull appearance shall not constitute grounds for rejecting parts.
Hot dip galvanized washers tend to bond to each other and suitable acceptance criteria should be agreed upon at the time of ordering.
The local coating thickness shall be a minimum of 40 !-1m and the batch average coating thickness
shall be a minimum of 50 !-1m. The measurement of the local coating thickness shall be made on
measuring areas as shown in Figure 3.
Measurement of the local coating thickness shall be conducted by the magnetic method in accordance
with ISO 2178 on every production lot.
To calculate the local coating thickness, a minimum of five readings shall be taken and averaged. In
case the geometry does not permit five readings, five samples shall be used to establish the
readings to be averaged. In case of dispute, the gravimetric method in accordance with
ISO 1460 shall be used. For the
calculation of the batch average coating thickness, the surface area of the fastener can be
evaluated according to Annex D.
The zinc coating shall adhere tenaciously to the surface of the base metal. The method for testing the adherence is specified in Annex E.
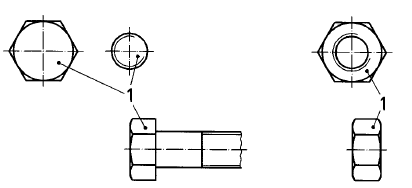
Key:
1. measuring area
Measuring area for local coating thickness measurement on fasteners
Lubrication
To enhance tightening behaviour of the assembly, the nuts or the bolts or the screws should be lubricated.
Ordering requirements
When ordering fasteners to be coated in accordance with this International Standard, the following
information shall be supplied to the coater:
a) reference to this International Standard and the coating designation (see Clause 11);
b) the material of the part, the manufacturing lot number and the condition of the part, e.g. heat
treatment, hardness or other properties, which may be affected by the
coating process;
c) whether a special coating thickness is required;
d) additional tests, if required;
e) additional treatments such as lubrication, chromating, etc., as required.
Other Informations
Terminology
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in ISO 2064 (in particular, the definitions of significant surface, measuring area, local thickness, minimum local thickness and average thickness) and the following apply.
quantity of identical parts cleaned, pickled, fluxed and galvanized together at one time in a galvanizing basket.
batches of parts originating from the same manufacturing lot, processed continuously through cleaning, pickling, fluxing, dipping in molten zinc and spun in a centrifuge without any change in temperature and concentration of the constituents of the process.
calculated average thickness of a coating as if it was uniformly distributed over the surface of the parts of the batch
process of heating parts for a definite time at a given temperature in order to minimize the risk of hydrogen embrittlement
process of heating parts for a definite time at a given temperature in order to relieve stress induced by work hardening
process whereby steel fasteners are zinc coated by immersion in a bath of molten zinc, resulting in the formation of a zinc-iron alloy coating or a zinc-iron alloy coating plus a zinc coating at the surface of the fastener
Normative Reference
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO 898-1, Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and al/oy steel - Part 1: Bolts, screws and studs
ISO 898-2, Mechanical properties of fasteners - Part 2: Nuts with specified proof load values - Coarse thread
ISO 965-1, ISO general purpose metric screw threads - Tolerances - Part 1: Principles and basic data
ISO 965-2, ISO general purpose metric screw threads - Tolerances - Part 2: Limits of sizes for general purpose external and internal screw threads - Medium quality
ISO 965-3, ISO general purpose metric screw threads - Tolerances - Part 3: Deviations for constructional screw threads
ISO 965-4, ISO general purpose metric screw threads - Tolerances - Part 4: Limits of sizes for hot-dip galvanized external screw threads to mate with internal screw threads tapped with tolerance position H or G after galvanizing
ISO 965-5, ISO general purpose metric screw threads - Tolerances - Part 5: Limits of sizes for internal screw threads to mate with hot-dip galvanized external screw threads with maximum size of tolerance position h before galvanizing
ISO 1460, Metallic coatings - Hot dip galvanized coatings on ferrous materials - Gravimetric determination of the mass per unit area
ISO 1461, Hot dip galvanized coatings on fabricated iron and steel articles - Specifications and test methods
ISO 2064, Metallic and other inorganic coatings - Definitions and conventions concerning the measurement of thickness
ISO 2178, Non-magnetic coatings on magnetic substrates - Measurement of coating thickness - Magnetic method
ISO 8991 Designation system for fasteners